Jakoba
Ultrastructure
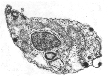 An oblique section of the cell
shows the anterior flagellar insertion
and the positions of major organelles. Food vacuoles contain
ingested bacteria. Extrusomes are small organelles on the cell
periphery that have ejectable contents; when viewed at just the
right angle, the extrusomes of Jakoba seem to have
vase-shaped contents. A single Golgi body/dictyosome lies next to the
flagellar bases (not visible in this image).
An oblique section of the cell
shows the anterior flagellar insertion
and the positions of major organelles. Food vacuoles contain
ingested bacteria. Extrusomes are small organelles on the cell
periphery that have ejectable contents; when viewed at just the
right angle, the extrusomes of Jakoba seem to have
vase-shaped contents. A single Golgi body/dictyosome lies next to the
flagellar bases (not visible in this image).
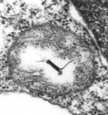 The
single mitochondrion is located next to, and mostly posterior to,
the nucleus. The cristae are irregular in shape, sometimes appearing
tubular as in the image above, or flattened as in the image at left. The
nucleoid is
the region of the mitochondrion that contains the DNA. It is not
always visible in mitochondria sectioned for the transmission microscope;
they can be viewed more reliably in the epifluorescence microscope with
suitable dyes.
The
single mitochondrion is located next to, and mostly posterior to,
the nucleus. The cristae are irregular in shape, sometimes appearing
tubular as in the image above, or flattened as in the image at left. The
nucleoid is
the region of the mitochondrion that contains the DNA. It is not
always visible in mitochondria sectioned for the transmission microscope;
they can be viewed more reliably in the epifluorescence microscope with
suitable dyes.
 The cytoskeleton is an asymmetrical
system of two flagellar bases,
two (or three) ventral microtubular roots, and a dorsal fan of secondary
microtubules. The "dorsal fan" microtubule arrangement is also found in
Reclinomonas and
Histiona. In Malawimonas, the
dorsal
fan microtubules are subtended by a two-stranded microtubular root arising
from the anterior basal body. The
left ventral root is associated with a multilayered structure, as in
Reclinomonas and Histiona but not Malawimonas. Most
of the microtubules that form the floor
of the ventral groove come from the left ventral root, again as in
Reclinomonas and Histiona but not Malawimonas, in
which most of the ventral groove microtubules comes from the right root.
The cytoskeleton is an asymmetrical
system of two flagellar bases,
two (or three) ventral microtubular roots, and a dorsal fan of secondary
microtubules. The "dorsal fan" microtubule arrangement is also found in
Reclinomonas and
Histiona. In Malawimonas, the
dorsal
fan microtubules are subtended by a two-stranded microtubular root arising
from the anterior basal body. The
left ventral root is associated with a multilayered structure, as in
Reclinomonas and Histiona but not Malawimonas. Most
of the microtubules that form the floor
of the ventral groove come from the left ventral root, again as in
Reclinomonas and Histiona but not Malawimonas, in
which most of the ventral groove microtubules comes from the right root.
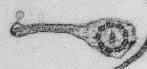 The posterior flagellum possesses a conspicuous and characteristic
flagellar vane. This vane arises on the dorsal surface of the
flagellum as in Reclinomonas (from which this figure is taken) and
Histiona; in Malawimonas, the vane
arises on the ventral surface.
The posterior flagellum possesses a conspicuous and characteristic
flagellar vane. This vane arises on the dorsal surface of the
flagellum as in Reclinomonas (from which this figure is taken) and
Histiona; in Malawimonas, the vane
arises on the ventral surface.
Return to summary information
 An oblique section of the cell
shows the anterior flagellar insertion
and the positions of major organelles. Food vacuoles contain
ingested bacteria. Extrusomes are small organelles on the cell
periphery that have ejectable contents; when viewed at just the
right angle, the extrusomes of Jakoba seem to have
vase-shaped contents. A single Golgi body/dictyosome lies next to the
flagellar bases (not visible in this image).
An oblique section of the cell
shows the anterior flagellar insertion
and the positions of major organelles. Food vacuoles contain
ingested bacteria. Extrusomes are small organelles on the cell
periphery that have ejectable contents; when viewed at just the
right angle, the extrusomes of Jakoba seem to have
vase-shaped contents. A single Golgi body/dictyosome lies next to the
flagellar bases (not visible in this image).  The
single mitochondrion is located next to, and mostly posterior to,
the nucleus. The cristae are irregular in shape, sometimes appearing
tubular as in the image above, or flattened as in the image at left. The
nucleoid is
the region of the mitochondrion that contains the DNA. It is not
always visible in mitochondria sectioned for the transmission microscope;
they can be viewed more reliably in the epifluorescence microscope with
suitable dyes.
The
single mitochondrion is located next to, and mostly posterior to,
the nucleus. The cristae are irregular in shape, sometimes appearing
tubular as in the image above, or flattened as in the image at left. The
nucleoid is
the region of the mitochondrion that contains the DNA. It is not
always visible in mitochondria sectioned for the transmission microscope;
they can be viewed more reliably in the epifluorescence microscope with
suitable dyes. The cytoskeleton is an asymmetrical
system of two flagellar bases,
two (or three) ventral microtubular roots, and a dorsal fan of secondary
microtubules. The "dorsal fan" microtubule arrangement is also found in
Reclinomonas and
Histiona. In Malawimonas, the
dorsal
fan microtubules are subtended by a two-stranded microtubular root arising
from the anterior basal body. The
left ventral root is associated with a multilayered structure, as in
Reclinomonas and Histiona but not Malawimonas. Most
of the microtubules that form the floor
of the ventral groove come from the left ventral root, again as in
Reclinomonas and Histiona but not Malawimonas, in
which most of the ventral groove microtubules comes from the right root.
The cytoskeleton is an asymmetrical
system of two flagellar bases,
two (or three) ventral microtubular roots, and a dorsal fan of secondary
microtubules. The "dorsal fan" microtubule arrangement is also found in
Reclinomonas and
Histiona. In Malawimonas, the
dorsal
fan microtubules are subtended by a two-stranded microtubular root arising
from the anterior basal body. The
left ventral root is associated with a multilayered structure, as in
Reclinomonas and Histiona but not Malawimonas. Most
of the microtubules that form the floor
of the ventral groove come from the left ventral root, again as in
Reclinomonas and Histiona but not Malawimonas, in
which most of the ventral groove microtubules comes from the right root.
 The posterior flagellum possesses a conspicuous and characteristic
flagellar vane. This vane arises on the dorsal surface of the
flagellum as in Reclinomonas (from which this figure is taken) and
Histiona; in Malawimonas, the vane
arises on the ventral surface.
The posterior flagellum possesses a conspicuous and characteristic
flagellar vane. This vane arises on the dorsal surface of the
flagellum as in Reclinomonas (from which this figure is taken) and
Histiona; in Malawimonas, the vane
arises on the ventral surface.