Cryptomonas
Introduction:
Cryptomonas is a genus of small phytoflagellates. Species are common in
marine and freshwater plankton, but the cells often are not found in plankton samples because
the usual fixatives do not preserve them - hence the common name
cryptomonads
("hidden
flagellates"). The genus and its relatives have become notorious, because the cryptomonad
plastid is the vestige of a eukaryotic endosymbiont, and because the confusing assemblage of
structural features that cryptomonads possess has made it difficult to establish the
phylogenetic relationships of the group.
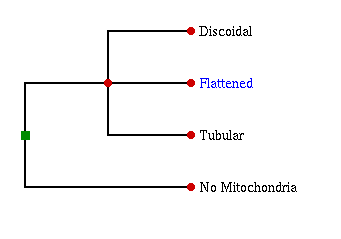
Postulated global eukaryote phylogeny based on presence or (ancestral) absence of
mitochondria, and shape of mitochondrial cristae. Cryptomonas belongs to the flattened
clade.
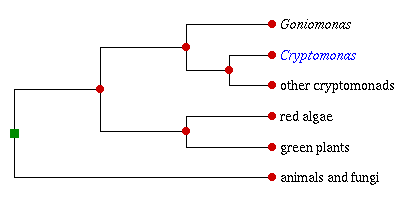
Postulated phylogenetic position of Cryptomonas, inferred from molecular and morphological
data. Branch lengths are arbitrary and do not reflect phylogenetic distance.
Return to summary information

