Trimastix
Ultrastructure
Trimastix trophic cells are "naked"; that is, no
conspicuous cell covering is found on cell body or flagella.
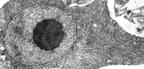 The single nucleus in a Trimastix cell
contains a conspicuous central nucleolus. This is the standard condition
for most protists, however many protozoa that look like, and
may be confused with, Trimastix species do not have this feature.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum surrounds
the nucleus and forms an organized array extending towards the posterior
end of the cell. Compare the
epifluorescence image The single nucleus in a Trimastix cell
contains a conspicuous central nucleolus. This is the standard condition
for most protists, however many protozoa that look like, and
may be confused with, Trimastix species do not have this feature.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum surrounds
the nucleus and forms an organized array extending towards the posterior
end of the cell. Compare the
epifluorescence image |
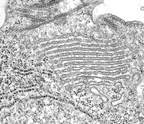 The Golgi apparatus consists of a
single membrane stack ("dictyosome"). The dictyosome is located adjacent
to the basal bodies of the kinetid. The cis face of the dictyosome
is oriented towards the cell membrane, the trans face towards the
nuclear envelope. This orientation is somewhat unusual, but it is also
found in the jakobid flagellates. The Golgi apparatus consists of a
single membrane stack ("dictyosome"). The dictyosome is located adjacent
to the basal bodies of the kinetid. The cis face of the dictyosome
is oriented towards the cell membrane, the trans face towards the
nuclear envelope. This orientation is somewhat unusual, but it is also
found in the jakobid flagellates. Retortamonad protists look like, and
may be confused
with, Trimastix, but in retortamonads, endoplasmic reticulum
and Golgi stacks cannot be shown by "routine" transmission
electron microscopy or fluorescent lipid labelling. Compare the
epifluorescence image
|
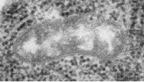 Mitochondria are absent. Cells have a few
small double-membrane-bound structures scattered throughout the
cytoplasm. These structures have been identified, tentatively,
as hydrogenosomes, but
the biochemical makeup and the function of these bodies is
unknown. Mitochondria are absent. Cells have a few
small double-membrane-bound structures scattered throughout the
cytoplasm. These structures have been identified, tentatively,
as hydrogenosomes, but
the biochemical makeup and the function of these bodies is
unknown. |
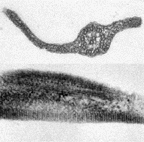 The posterior
flagellum in trophic cells possesses two
conspicuous and characteristic flagellar vanes, arising on opposite sides
of the flagellum near its insertion into the cell. Each vane has a
striated substructure, especially near the margin of the vane. The
position and structure of the vanes is similar to jakobids, where only one
vane is present, and in retortamonads where two are found. The function
of the vanes is not known, but the best guess is that it is involved in
establishing water currents through the ventral groove, through which the
bacteria upon which Trimastix feeds are passed. The posterior
flagellum in trophic cells possesses two
conspicuous and characteristic flagellar vanes, arising on opposite sides
of the flagellum near its insertion into the cell. Each vane has a
striated substructure, especially near the margin of the vane. The
position and structure of the vanes is similar to jakobids, where only one
vane is present, and in retortamonads where two are found. The function
of the vanes is not known, but the best guess is that it is involved in
establishing water currents through the ventral groove, through which the
bacteria upon which Trimastix feeds are passed. |
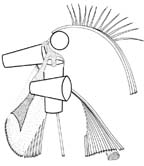 The cytoskeleton is an asymmetrical system
of four flagellar bases, a dorsal (anterior) and three ventral microtubular
roots, and secondary cytoskeletal microtubules arising from the anterior
root and forming a "fan" along the dorsal surface of the cell. The
ventral roots extend to the posterior cell, where they terminate at a
common point. These roots define the margins and the floor of the
ventral groove. The kinetid of Trimastix marina is slightly
more complex than are the kinetids in the other Trimastix
species that have been studied. The cytoskeleton is an asymmetrical system
of four flagellar bases, a dorsal (anterior) and three ventral microtubular
roots, and secondary cytoskeletal microtubules arising from the anterior
root and forming a "fan" along the dorsal surface of the cell. The
ventral roots extend to the posterior cell, where they terminate at a
common point. These roots define the margins and the floor of the
ventral groove. The kinetid of Trimastix marina is slightly
more complex than are the kinetids in the other Trimastix
species that have been studied.
The Trimastix kinetid is similar to those of jakobids and
retortamonads. The motif of left, intermediate and right ventral roots
extending in parallel from the basal bodies to the posterior end of the
cell and defining a ventral groove, is not found in other protists.
Trimastix shares with Malawimonas the presence of an anterior root with
associated microtubules, the addition of microtubules to the inside of the
left root, and the absence of a laminate structure below the left root.
In other jakobids (Jakoba, Histiona and Reclinomonas),
and in the retortamonads, the anterior root is absent, microtubules
are added to the outside of the left root, and a laminate
structure (MLS) is present below the left root. |
Return to summary information
 The single nucleus in a Trimastix cell
contains a conspicuous central nucleolus. This is the standard condition
for most protists, however many protozoa that look like, and
may be confused with, Trimastix species do not have this feature.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum surrounds
the nucleus and forms an organized array extending towards the posterior
end of the cell. Compare the
epifluorescence image
The single nucleus in a Trimastix cell
contains a conspicuous central nucleolus. This is the standard condition
for most protists, however many protozoa that look like, and
may be confused with, Trimastix species do not have this feature.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum surrounds
the nucleus and forms an organized array extending towards the posterior
end of the cell. Compare the
epifluorescence image 


